Digital Oracles Explained: Bridging the Gap Between Blockchains and the External World
Ever wondered how the isolated world of blockchain talks to the outside universe? Dive into the intriguing world of digital oracles and discover the secret agents of data that bridge the gap!
A blockchain operates within a confined environment, with minimal interaction points with the external world. Oracles step in as external data couriers, ferrying off-chain data into the realm of the blockchain.
Before we dive headfirst into the highbrow world of oracles, let's take a moment to appreciate the conundrum they're here to unravel. Picture oracles as the tech world's diplomats, smoothing out the relations between the hermit kingdom of blockchains (on-chain) and the bustling metropolis of external data sources (off-chain).
Now, most blockchains come with their own cryptocurrencies, the golden tickets that make everything from value transfers and protocol operations to governance possible. Some even support smart contracts — think of these as autonomous robots inside the blockchain protocol, tirelessly working to carry out a predetermined set of actions once certain conditions are met.
Let's take an example — weather-based insurance contracts. You could program a smart contract to read something like, "If rainfall in location X exceeds Y millimeters on date Z, then shower policyholder A with the insurance amount." The smart contract, ever the obedient servant, executes the command in an unalterable manner, making traditional third-party intermediaries as obsolete as a floppy disk.
But there's a catch. For these smart contracts to work their magic in real-life situations, they need a way to integrate with off-chain data. Like, how much rain did fall that day? Apparently, blockchains, with their introverted nature, can't access this data directly. Enter oracles, the bridge between the blockchain kingdom and the outside world.
👉 TL;DR: Given that blockchains and smart contracts are isolated systems, oracles provide a secure method of feeding off-chain data into a blockchain network's on-chain milieu.
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
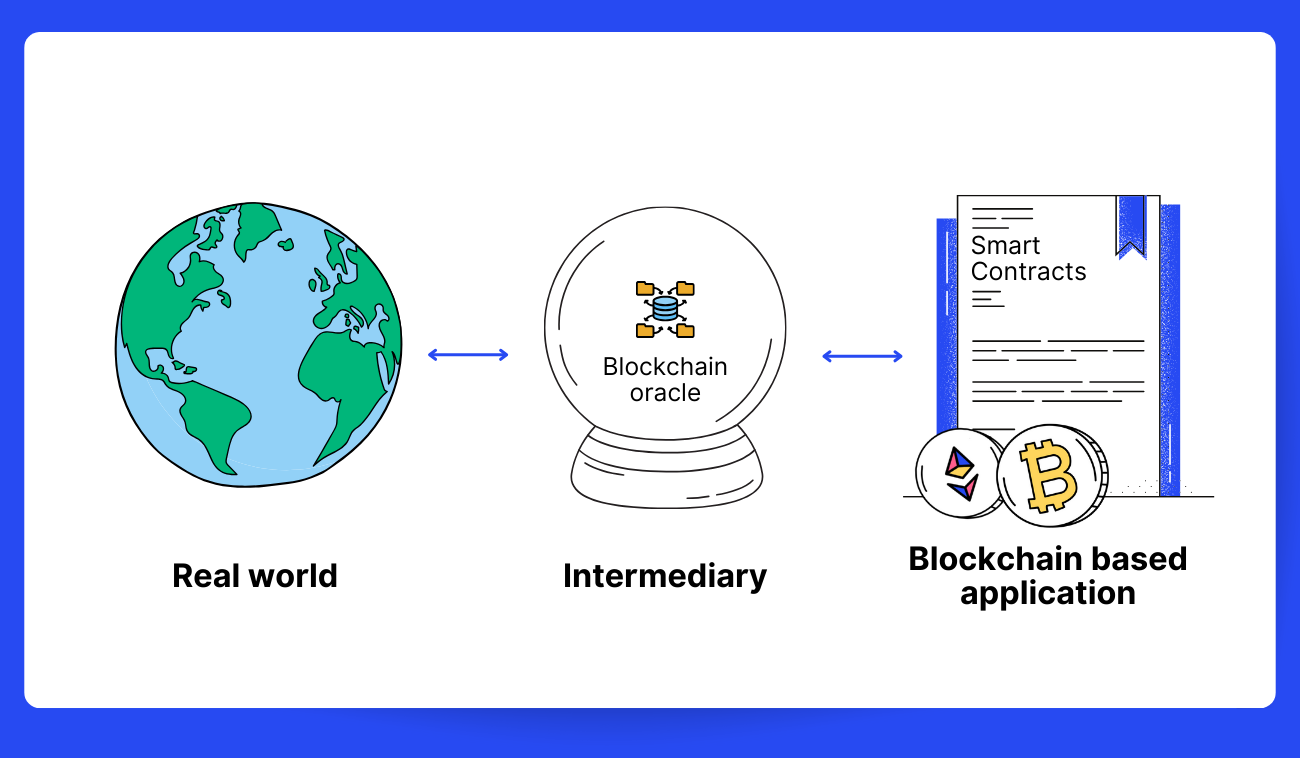
A blockchain oracle is akin to a data courier, delivering external information to the blockchain's smart contracts (Pic. 1).
👉 Think of an oracle as a scout in the realm of blockchains and cryptocurrencies, tasked with finding and verifying real-world events, then reporting them back to the blockchain for smart contracts to utilize.
Oracles come in different flavors, categorized by the type of data they handle, their data source, and their degree of centralization:
- Data type oracles: These are like specialists in a particular field, be it price oracles, weather oracles, and so forth.
- Source-based oracles: Among these, we have software oracles sourcing data from online, while hardware oracles — sensors or similar physical devices — pipe data straight into the blockchain.
- Centralization-based oracles: Here, the centralized variety is governed by a single entity, while decentralized oracles spread the power among multiple entities to keep manipulation risks at bay.
Oracles serve as the lifeblood for numerous decentralized applications (DApps) operating on blockchain networks. But they're not without their flaws. They bring trust into a system that's otherwise trust-averse. If an oracle feeds false or twisted information, it can wreak havoc on the smart contracts depending on it. This predicament is famously dubbed the "oracle problem," and numerous brainiacs are burning the midnight oil to figure out a way around this conundrum.
How Digital Oracles Work
Every oracle has a triad of core responsibilities:
- Keep an ear to the ground for any requests for external data within the blockchain network;
- Mine the requested data from external systems;
- Relay the unearthed data back to the smart contracts.
Oracles can act as intermediaries for cross-chain chatter or as couriers, delivering data from a centralized system to a blockchain. While one oracle may be busy transferring data to a blockchain, another might be hobnobbing with external ecosystems.
Ways to Set Up an Oracle
Setting up an oracle can be accomplished in three primary ways, each with its own unique flair:
- Immediate-read
In the fast-paced world of immediate-read oracles, information is provided solely for quick, spur-of-the-moment decisions. For instance, Does this car have a valid insurance?" Those who need to query such information usually do it in a "just-in-time" fashion, meaning the search is only conducted when the information becomes necessary.
Examples of this type of oracle could be license plate numbers, professional certifications, club memberships, airline identification, amongst others. It's all about the quick draw of data!
- Publish-subscribe
This kind of oracle essentially provides a data broadcasting service for information that's prone to regular and frequent changes. Imagine a smart contract on-chain anxiously polling the oracle or an off-chain daemon eagerly watching for updates.
Weather data, price feeds, economic or social statistics, and traffic data are just a few examples of the publish-subscribe setup.
- Request-response
Now we've reached the most challenging category: request-response. Here's where the data space is simply too enormous to be stored in a smart contract. Users are only expected to use a tiny fraction of the entire information at any given time. It's also a shrewd business strategy for data providers.
In practical terms, this type of oracle may be realized as a system of on-chain smart contracts and off-chain infrastructure that constantly monitors requests and retrieves and returns data. When a decentralized application makes a data request, it often kicks off an asynchronous process with multiple steps.
Centralized vs Decentralized Oracles
Up until 2017, the market was dominated by centralized solutions. A sudden hiccup in these systems could leave the blockchain in a data drought, impacting thousands of users and potentially freezing their funds in smart contracts.
👉 To paint a clearer picture, let's take an example: Picture a place where the weather flip-flops more than a politician. The only weather forecast comes from a service aptly named "Weather." Now, if "Weather" has a meltdown, people are left guessing whether they should dress for a beach day or a blizzard.
Decentralized oracles bypass such predicaments, drawing data from a plethora of sources simultaneously. This data is then shared among all oracles, resulting in each oracle having information that's been cross-verified by its peers.
To drive the point home, let’s take a look at another, real example.
The Compound platform allows users to take out loans in digital currencies, where they can pledge one type of cryptocurrency to receive another. This borrowed crypto can then be used as the user sees fit. It's all fun and games until the price of the loan starts to outpace the collateral due to a sudden price increase. Then, our trusty friend the smart contract steps in and automatically liquidates it.
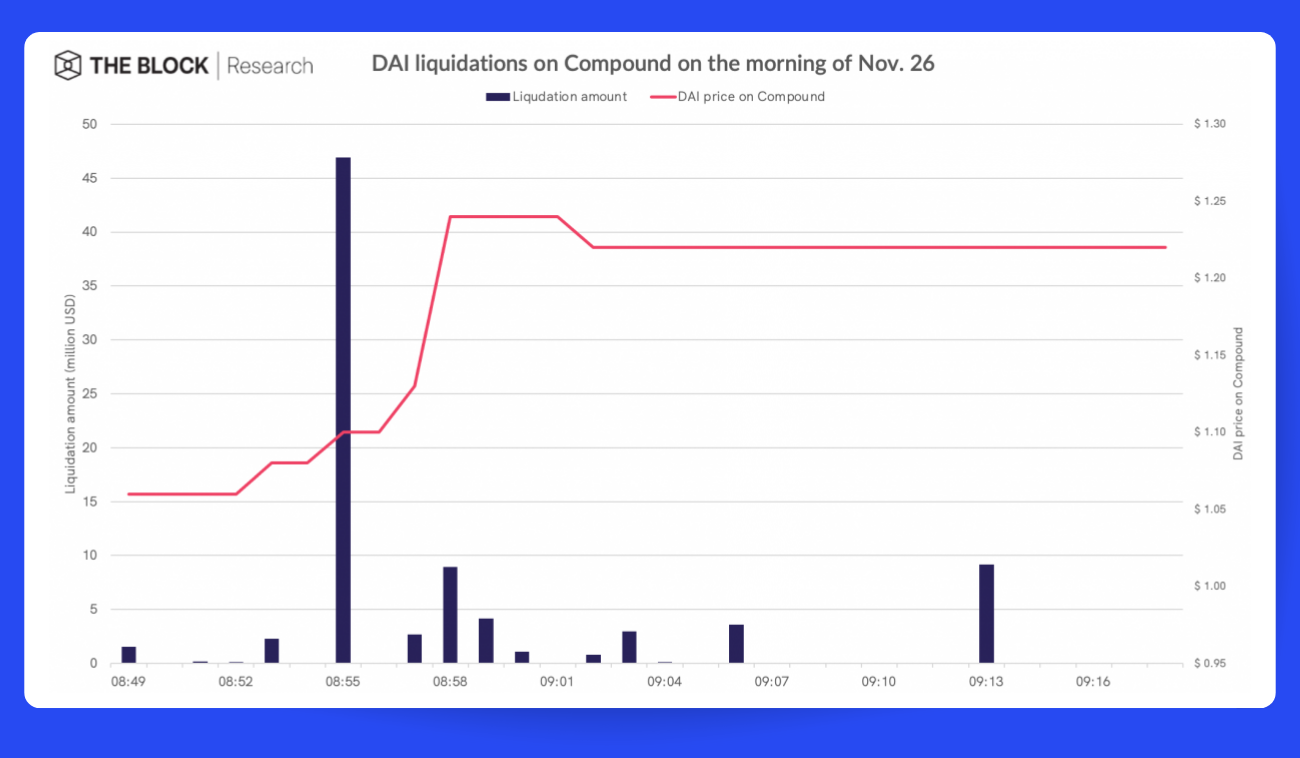
Isn't it just peachy when relying on a single, centralized source of information leads to significant losses? In this case (Pic. 2), users of the Compound protocol waved goodbye to nearly $100 million.
Our friend Compound was pulling data for the DAI stablecoin from one solitary information source — the digital currency exchange, Coinbase Pro. Then, on one fateful day in November 2020, DAI decided to take a joyride on Coinbase Pro and its price skyrocketed to $1.30.
Like a domino effect, the value of the loans exceeded their collaterals, leading to a cascade of automatic liquidations totaling a whopping $88.4 million. As if that wasn't enough, it also messed with the dYdX decentralized protocol’s workflow causing an additional loss of about $8 million.
Now, imagine if Compound had used oracles pulling data from multiple sources. This whole fiasco could have been avoided! A decentralized oracle would have noticed the unusual DAI price surge on a single exchange, shrugged its shoulders, and moved on.
In today's world, where DeFi projects are popping up like mushrooms after the rain, oracles are the new black. They ensure protocols always have the latest market gossip, allowing investors to trade within smart contracts without the need for those old-fashioned exchanges.
Without these superstar decentralized oracle services, it's doubtful we would have the current total value locked (TVL). These oracles are like the social butterflies of the blockchain world, bridging the gap between on-chain and off-chain systems, allowing them to exchange data and open new doors for blockchain technology.
However, let's not get carried away. While decentralized oracles might seem like the superhero of the system, they don't have an answer for everything. Market anomalies can still throw a wrench in the works, and designing systems that can handle these anomalies is a game of 4D chess.
Examples of Blockchain Oracles
Let’s take a look at the most prominent examples of oracle service providers.
Chainlink
Chainlink is the heavyweight champion of the blockchain oracle universe. It orchestrates off-chain information for a broad spectrum of blockchain-based ensembles: from layer-1s and layer-2s to sidechains, and even the most niche DApps strutting their stuff on smart contracts. Birthed in 2019 as an Ethereum-based oracle by the software wizards at San Francisco's SmartContract, Chainlink got a powerful boost in December 2021 when Eric Schmidt, previously the big boss at Google, came onboard as a strategic advisor for upcoming adventures.
Chainlink bestows its oracular gifts on a plethora of blockchain platforms and software firms, including Avalanche, Aave, Ampleforth, Compound, Swisscom, and T-Systems, just to name a few.
In a nutshell, Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that ensures data transfer doesn't get lost in translation. And to make this happen, Chainlink relies on a team (or network) of nodes that fetch data from various sources (Pic. 3). These nodes then pool this data together and deliver it to smart contracts, triggering their execution.
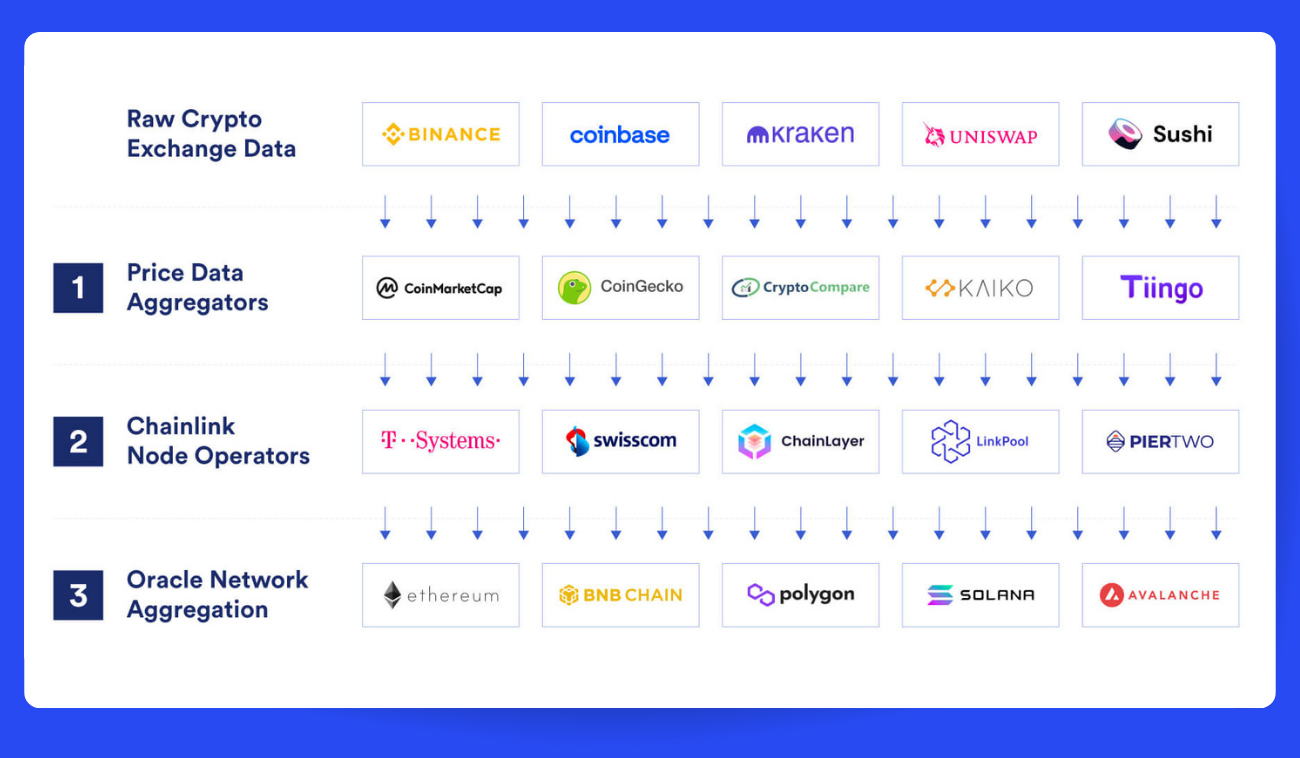
Chainlink is quite the versatile system, supporting a plethora of data types, from Wall Street market data to weather forecasts. Smart contract developers can essentially order their data à la carte from the oracles.
The Chainlink Verified Random Function and Chainlink Automation, two dynamic features at the heart of Chainlink, support its reputation as a top-notch blockchain oracle.
API3
API3 is a democratic oracle managed by its community, enabling users and developers from blockchain applications or businesses to hitch their Web3 apps to the platform. This grants them access to a cascade of off-chain data from a diverse range of markets, including but not limited to stocks, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and more.
API3 takes a unique approach by employing dAPIs, or decentralized application programming interfaces. Unlike its oracle peers that resort to oracle nodes as middlemen to hunt, interrogate, and deliver data, API3 sources data directly from the horse's mouth, the first-party sources.
A noteworthy aspect of API3 is the Airnode, a Web3 middleware that links web APIs directly to any blockchain application. This magical bridge makes any API compatible with blockchain technology.
API3 has a pretty impressive contact list, with names like Fantom, Polygon, Digital Currency Group, AllianceBlock, and more.
Band Protocol
Band Protocol is a cross-chain oracle that has set up shop on Cosmos, a bustling hub of interoperable networks. It feeds unalterable data into smart contracts with the help of its public blockchain, BandChain.
The validators on BandChain are like data couriers, fetching information from APIs and other web sources and delivering this precious cargo to users and entities. Thanks to the magic of Cosmos' IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) protocol, the Band Protocol can shuttle data to a variety of blockchains. Users can also get creative and script their own oracle to pull in data streams from the real world, covering a broad spectrum from stock and asset markets to commodities and cryptocurrencies, and even real-life happenings like weather patterns or the latest sports scores.
Band Protocol has managed to woo some big names in the industry, counting Binance, Fantom, Moonriver, and Iron Bank among its backers and integrations.
Start Trading Crypto on Bitsgap
Now that you've dipped your toes into the world of oracles, why not venture a bit further and explore the Bitsgap platform for trading crypto and raking in some additional passive income via an affiliate program and competitions?
By linking up your exchange accounts (up to 17 of them, no less), you can become a trading maestro, managing all your exchanges from a single, streamlined interface, bidding farewell to the chaos of juggling multiple platforms.
But there's more — a treasure trove of smart trading tools awaits you! With automated trading bots like GRID, DCA, BTD, or COMBO at your disposal, and a toolkit filled with the Technicals widget and a variety of charting instruments, you can confidently chart your path to crypto market success.
Give it a whirl today and enjoy a seven-day free trial on the PRO plan!
Bottom Line
Think of blockchain oracles as often overlooked heroes, valiantly bridging the gap between the fantasy world of blockchain and the mundane real world. Without them, smart contracts would be about as smart as a sack of potatoes, completely oblivious to actual data.
From those oh-so-trendy NFTs and gaming to the cut-and-dry practicalities of insurance and supply chains, our oracle friends have their fingers in every pie.
Of course, they're not perfect. Their security and reliability are vital for sustaining the integrity and operational efficiency of the systems that depend on them.
FAQs
What Are Blockchain Oracles?
Also known as blockchain middleware, blockchain oracles serve as a bridge linking blockchains with external (off-chain) clients and services.
These oracles play the role of a go-between, facilitating the interaction between blockchains and external data sources. They establish communication channels for the exchange of information from blockchains to third-party services, and the reverse.
What Are Decentralized Oracles?
Decentralized oracles are engineered to address the shortcomings of centralized oracles by removing any single point of failure. A decentralized oracle service consists of multiple members in a peer-to-peer network that reach a consensus on off-chain data prior to feeding it into a smart contract.
