
Perfect Your Trading With Triggers
Take the emotion and stress out of crypto trading with simple "if this, then that" trigger sets. Explore the benefits of trigger trading.
Trigger trading — executing trades automatically based on predefined market conditions — is especially impactful in crypto's volatile landscape. By rapidly responding to price shifts, managing risk, and capturing chances sans manual oversight, this strategy optimizes efficiency and profitability.
Considering crypto's signature volatility, trigger trading progresses from useful to near-essential. For traders seeking to maximize returns through fluctuating markets, it brings automation to opportunity.
This article will unpack trigger trading's concepts, deliver real-world implementations, and showcase how Bitsgap's platform specifically elevates this high-powered tactic. From comprehensible overview to platform-specific advantage, we will explore how trigger trading can evolve from concept to optimized crypto success.
What Is a Trigger Price in Crypto?
A trigger price in cryptocurrency trading refers to a predefined price level that, once reached, activates a specific trade order. This concept is commonly used in various types of orders to help traders manage risk and enter or exit the market at predetermined price points.
Here’s how it typically works in different scenarios:
- Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order has a trigger price set by the trader, which, when reached, converts the order into a market order. The primary purpose is to limit potential losses on a position. For example, if a trader buys Bitcoin at $40,000 and sets a stop-loss order with a trigger price of $38,000, the order will execute and sell the Bitcoin as soon as the price drops to $38,000, thus preventing further losses.
- Take-Profit Orders: Similar to stop-loss orders but used to secure profits, a take-profit order has a trigger price that, when reached, will close the position to capture the gains. If the trader sets a take-profit order at $45,000 after buying at $40,000, the trade will automatically close when Bitcoin hits the $45,000 mark.
- Stop-Limit Orders: This type of order combines the features of stop-loss and limit orders. The trigger price here first converts the stop order into a limit order, not a market order. This gives the trader more control over the execution price but can also result in the order not being filled if the market price surpasses the limit price too quickly.
- Trailing Stops: A trailing stop order sets the trigger price at a fixed amount or percentage away from the market price. It adjusts as the price fluctuates, maintaining the set distance. This allows traders to protect gains while giving the position room to grow.
Using a trigger price effectively in trading strategies helps in managing risk, securing profits, and defining entry or exit points without needing to constantly monitor the market. It’s a crucial tool in cryptocurrency trading, where prices can change dramatically in a short period.
What Is Trigger Trading?
Trigger trading is the broader concept encompassing the use of automated systems to execute trades when certain predefined conditions or "triggers" are met. These triggers can be based on various inputs including but not limited to:
- Price Actions: Specific price points such as highs, lows, or breakout levels.
- Technical Indicators: Conditions derived from technical analysis tools like moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence).
- Economic Indicators: Reactions to macroeconomic reports or news events that are expected to impact market prices.
- Volume Triggers: Significant changes in trading volume that might indicate upcoming price movements.
The primary advantage of trigger trading is that it helps automate the decision-making process, removing emotional biases and ensuring that trades are executed at optimal moments based on objective criteria. This method also enables traders to manage their risk more effectively, as they can set specific conditions under which their positions are automatically closed, either to take profits or cut losses.
Trigger trading typically employs the use of trading platforms that support conditional orders and can handle complex algorithms. These platforms monitor market conditions in real-time and execute trades instantly when the defined triggers are activated.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Trigger Trading
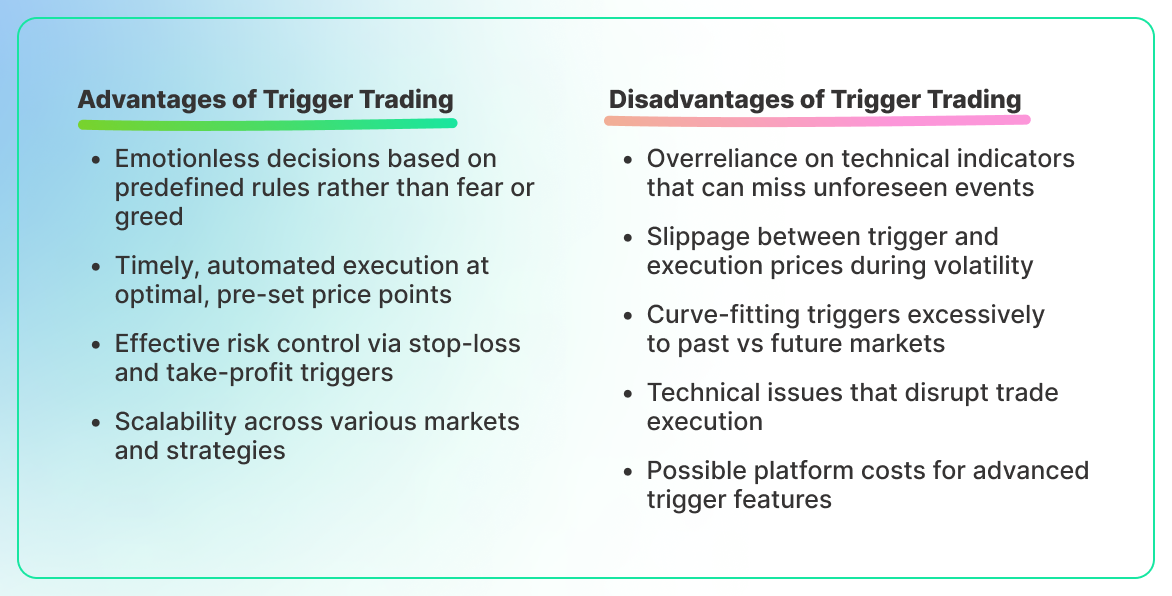
Trigger trading, like any trading strategy, comes with its set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help traders determine if trigger trading aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Advantages of Trigger Trading
- Emotionless Trading: By setting predefined triggers, traders can make decisions that are less influenced by emotions like fear and greed. This can help in maintaining discipline and sticking to a trading plan.
- Timely Execution: Trigger trading allows for the automatic execution of trades at specific price points or under certain conditions. This immediate action can be crucial in fast-moving markets, ensuring that opportunities are not missed and that entries and exits are executed at optimal levels.
- Risk Management: Traders can better manage risk by setting trigger points for stop-loss and take-profit orders. This helps in protecting gains and minimizing losses without the need to constantly monitor market movements manually.
- Efficiency: Trigger trading is time-efficient as it reduces the need for continuous market monitoring. Traders can set their trade conditions in advance and allow the system to handle execution.
- Scalability: This method allows traders to operate multiple strategies or trade across various markets simultaneously since the trading rules are handled by automated systems.
Disadvantages of Trigger Trading
- Dependency on Technical Analysis: Trigger trading often relies heavily on technical indicators which might not always account for sudden market changes due to unforeseen events or news. This can lead to potential misfires or unexpected losses.
- Slippage: In volatile markets, the actual execution price may differ from the trigger price due to slippage. This discrepancy can affect the expected profitability of trades.
- Over-Optimization: When creating triggers, there's a risk of over-optimizing them to past market conditions, which may not necessarily predict future movements accurately (also known as curve fitting).
- Technical Failures: Dependence on digital platforms means traders are susceptible to risks like connectivity issues, system failures, or software bugs, which can impede trade execution.
- Costs: Some advanced trading platforms that support sophisticated trigger trading options might come with higher fees or subscriptions, adding to the trading costs.
- Market Impact: Especially in smaller or less liquid markets, large trigger-based orders can themselves impact the market price, potentially moving the price in an unfavorable direction before the full execution of the trade.
Understanding these pros and cons can help traders decide whether trigger trading fits within their broader trading strategy and how best to implement it to maximize gains while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Trigger Trading Examples
Now, let’s examine trigger trading in crypto, using various trading scenarios and technical setups.
Trigger Trading Example # 1: Bitcoin Breakout Trade
Situation: You believe that Bitcoin will experience a significant price movement if it breaks out of its current resistance level.
Trigger Setup:
- Buy Stop Order: Place a buy stop order just above the resistance level at $60,000, anticipating a breakout.
- Stop-Loss Order: Set a stop-loss at $58,500 in case the breakout fails.
- Take-Profit Order: Set a take-profit at $62,000 to lock in gains.
Outcome: If Bitcoin’s price breaches $60,000, your buy stop order triggers, purchasing Bitcoin. If the price then climbs to $62,000, your take-profit triggers, selling Bitcoin and securing profits. If the price instead falls back to $58,500, the stop-loss triggers to minimize losses.
Trigger Trading Example # 2: Ethereum Rebound Trade Using Fibonacci Retracement
Situation: Ethereum is in a downtrend, but you expect it to rebound at a key Fibonacci retracement level.
Trigger Setup:
- Buy Limit Order: Place a buy limit order at the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level from the recent high, expecting support and a reversal.
- Stop-Loss Order: Set a stop-loss just below the 78.6% Fibonacci level to cut losses if the reversal does not occur.
- Take-Profit Order: Set a take-profit near the previous high, anticipating a full recovery.
Outcome: If Ethereum’s price hits the 61.8% Fibonacci level, your buy limit order triggers, buying Ethereum. If the price recovers to the previous high, your take-profit triggers, securing profit. If it breaks below the 78.6% level, your stop-loss triggers, limiting your downside.
Trigger Trading Example # 3: Ripple (XRP) Using RSI and MACD Crossover
Situation: You want to use technical indicators to determine optimal entry and exit points for XRP.
Trigger Setup:
- Buy Trigger: Set a buy trigger when the RSI is below 30 (oversold) and there is a bullish MACD crossover.
- Sell Trigger: Set a sell trigger when the RSI goes above 70 (overbought) or there is a bearish MACD crossover.
Outcome: The system monitors XRP and triggers a buy order when both conditions are met, suggesting a potential upside. It also places a sell order when the asset becomes overbought or the MACD indicates a downward movement, thus securing profits or preventing losses.
Trigger Trading Example # 4: Scalping Litecoin on Price Volatility
Situation: Litecoin shows high intraday volatility, and you want to scalp small profits.
Trigger Setup:
- Buy Trigger: Set a buy trigger if the price drops rapidly by 3% within an hour.
- Sell Trigger: Set a sell trigger for a 1.5% price increase from the buying price or a further 1% drop.
Outcome: Your trading system quickly buys Litecoin following a sharp drop and sells it either on a modest rebound for a quick profit or on a slight further drop to minimize losses. This strategy could involve numerous trades throughout the day, leveraging small price movements for gains.
Trigger Trading Example # 5: Long-Term Position on Chainlink with Price Alerts
Situation: You're bullish on Chainlink in the long term but want to buy on dips.
Trigger Setup:
- Buy Alert: Set a price alert if Chainlink drops 10% from its current price.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): Automatically buy a set dollar amount when the alert triggers.
- Long-Term Sell Trigger: Set a sell trigger at a price 50% above your average entry price.
Outcome: Receive alerts when Chainlink drops, triggering DCA buys, lowering your average buy-in price. If the price eventually rises significantly, your sell trigger executes, realizing a substantial gain.
Bitsgap’s Smart Trading
If you're in search of an automated trading platform that supports trigger trading, you might want to consider Bitsgap. More than just a standard trading platform, Bitsgap offers an integrated solution that includes automated trading bots, a smart trading terminal, portfolio management, and actionable analytics. In the following section, we will explore the smart trading features available on Bitsgap that can enhance your trading experience including trigger trading.
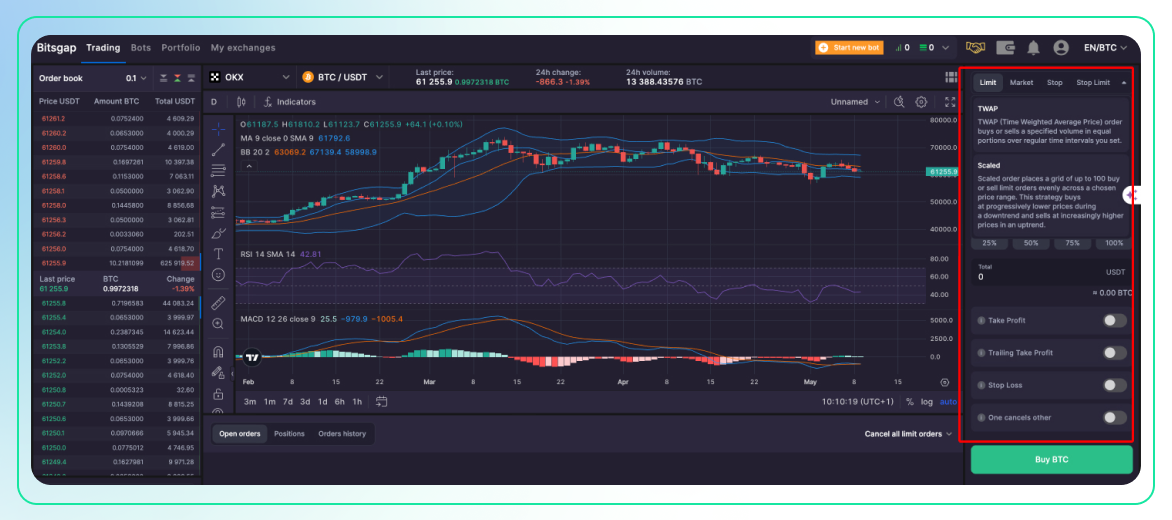
To begin with, Bitsgap offers a variety of order types, and any manual order placed on Bitsgap can be transformed into a smart order. The smart order options available include:
- TWAP: The algorithm breaks up the order into smaller chunks and executes these smaller orders at regular intervals over a specified period. The goal is to ensure that the average price of all executed chunks is as close as possible to the average price of the asset over the same period, thus minimizing market impact.
- Scaled: Scaled order consists of several limit orders placed one by one in decreasing or increasing order of price. By scaling the order, the trader can potentially get a better overall entry or exit price spread over several smaller transactions, reducing the impact on the market and potentially benefiting from averaging the prices.
- OCO: A conditional order where two orders are placed simultaneously, and if one order is executed, the other is automatically canceled. This is useful for setting up a strategy where you want to take profits at a certain price but also want to limit your losses if the market moves in the opposite direction.
- Stop Market: A type of stop order that becomes a market order once a specified price level, known as the stop price, is reached. It is used to limit losses or protect profits on a position. Unlike a limit order, a stop market order does not guarantee the execution price; once triggered, it will be executed at the best available price in the market, which can be significantly different from the stop price during periods of high volatility.
- Stop Limit: Combines the features of a stop order and a limit order. It has two prices: the stop price, which converts the order to a live limit order, and the limit price, which is the worst price at which the order should be executed. This type of order allows more control over the price at which the order is executed compared to a stop market order, but it does not guarantee execution if the market price bypasses the limit price without filling the order.
As mentioned, any order can be augmented with various conditions, including triggers. For instance, in the following example (Pic. 2), a standard sell limit order for BTC is shown, enhanced with multiple features including two distinct take profit levels at 2% and 6%, a trailing take profit of 3% with a 0.2% distance, and a stop loss of 1%.
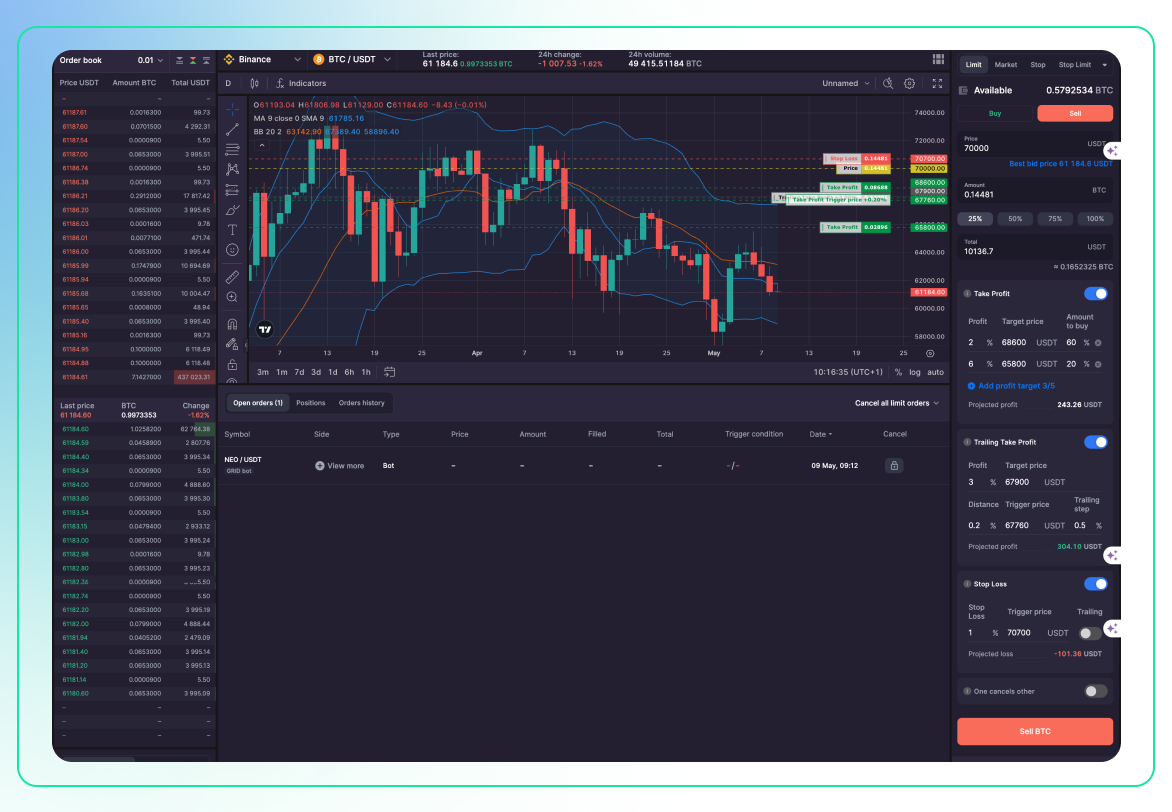
Trailing Take Profit (TTP) serves as an excellent illustration of trigger trading in practice. It is a dynamically adjustable order set up to capture price increases and maximize profits. TTP aims to enhance your profits by allowing a trade to remain open as long as the price continues to move favorably. The order is executed when the price reaches the trailing profit level.
When setting your TTP, you first establish your target price—this is the initial placement of the TTP, which is activated if the price reaches this level. Next, you set the Trigger price—this activates the TTP. The price must reach this level for the TTP to be set at the Target price. You also need to determine the Trailing step by specifying the percentage (%) of the price step, which dictates how frequently the TTP adjusts to follow the price movements. For instance, a trailing step of 0.5% in the example above means the TTP is adjusted every time the price changes by 0.5%.
Trailing Take Profit is particularly effective when used in conjunction with a Take Profit order. This approach not only distributes the amount among your Take Profit orders but also reserves some coins to maximize gains through TTP. TTP will sell your coins at the most advantageous price by tracking the price movements either upward or downward, depending on your settings. In the example provided, the Take Profit orders execute sales of a predetermined amount of coins at set prices, leaving the remainder for TTP to enhance profits as the price rises. This strategy allows you to fully capitalize on potential profits by letting the trailing feature adjust your Trailing Take Profit, executing it when the price retraces.
Another application of TTP is to incorporate it into Trailing Stop-Market buy order. As the market price decreases, the Stop-Market order with activated trailing will adjust the entry point downwards and execute the order when a price reversal occurs. Subsequently, the Trailing Take Profit will track the price as it climbs and execute the sell order when a price pullback occurs. This strategy enables you to buy the coin at the optimal price at the start of a rally and sell it at its peak as the price begins to decline.
But trigger trading is not only about manual setup. In fact, bots can follow triggers too (Pic. 3):
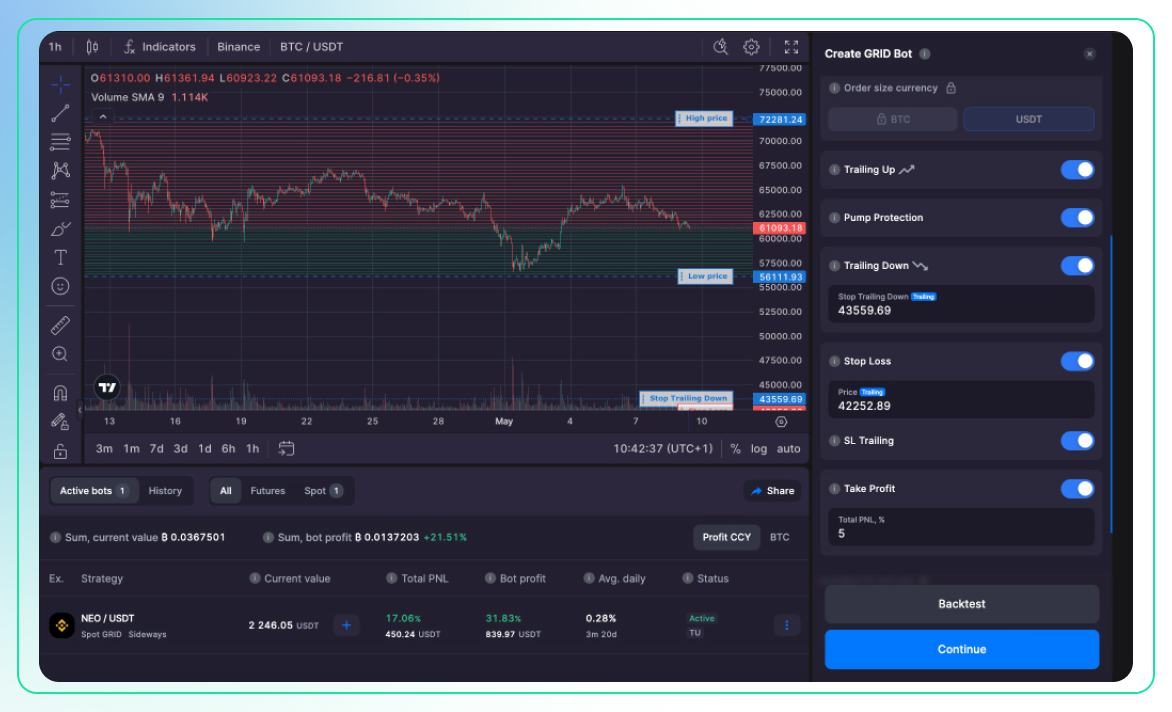
As illustrated above, Bitsgap’s bots offer a range of configurable settings, including enabling Trailing Up/Down, Stop-Loss Trailing, and setting up Take Profit and Stop Loss parameters.
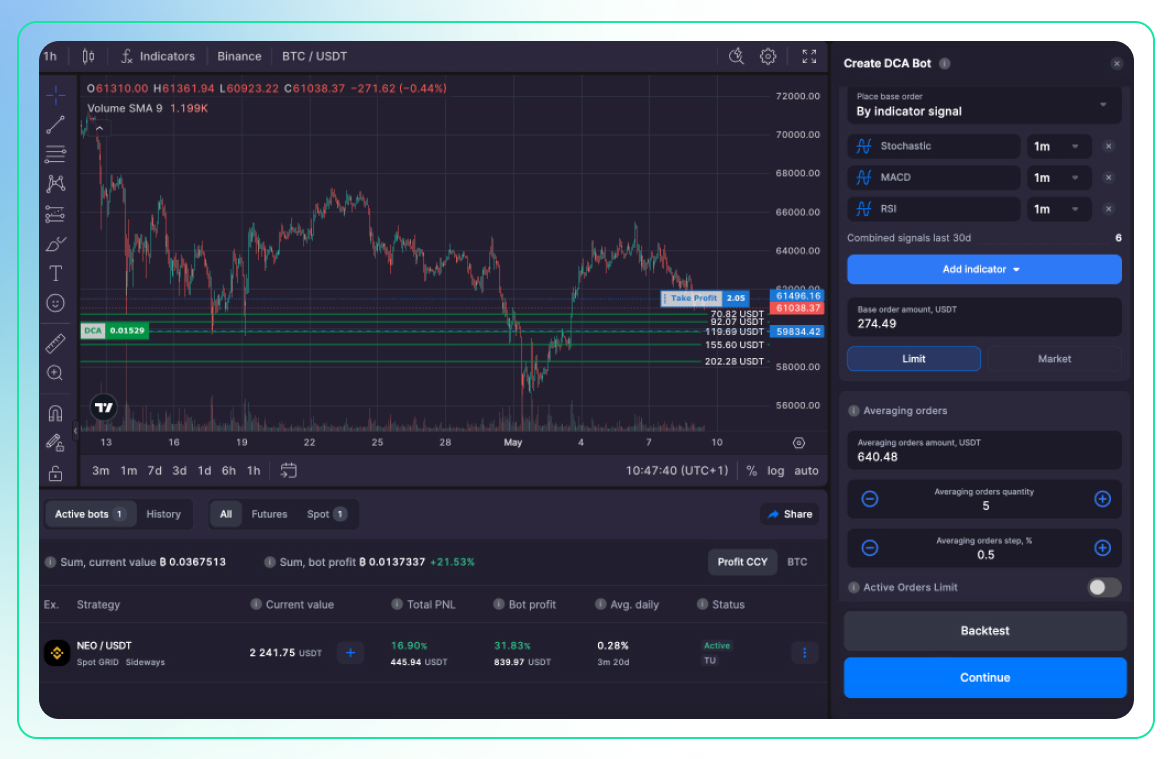
Furthermore, Bitsgap's DCA (Dollar Cost Averaging) can initiate or exit trades based on up to three technical indicators of your choice. Whenever one, two, or all of these indicators signal an optimal entry or exit point, the bot will act accordingly (Pic. 4):
You can explore all these features and more with a 7-day free trial of the PRO plan, which includes up to 275 bots, futures bots, take profit and stop loss for all bots, among other advanced features. After the trial, choose from any of our three-tier subscription plans to continue trading with Bitsgap’s advanced tools.
Conclusion
As discovered, trigger trading stands out as an indispensable tool in the arsenal of any cryptocurrency trader. By allowing for automated responses to specific market conditions, it not only conserves time and reduces the emotional strain of trading but also enhances decision-making precision and potential profitability. However, like any trading strategy, trigger trading comes with its own set of challenges. It requires a clear understanding of market indicators and the setting of appropriate triggers to avoid premature or unwanted executions. Additionally, relying solely on automated systems may lead to missed nuances that a manual review could catch.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of incorporating trigger trading into your strategy are significant, and the right tools can mitigate many of its drawbacks. Bitsgap offers a comprehensive platform with robust features designed to facilitate trigger trading effectively. With options like Stop Loss/Take Profit, Trailing Up/Down, Trailing Take Profit, Stop-Loss Trailing, and others, Bitsgap provides traders with the necessary tools to refine their trading strategies and maximize their outcomes. We invite you to sign up for Bitsgap and explore these powerful features, including the triggers themselves!
FAQs
What Are Trigger Trades?
Trigger trades refer to a trading strategy where specific predefined criteria or conditions, when met, initiate a buy or sell order automatically. This strategy is widely used in stock, forex, and cryptocurrency trading to capitalize on expected market movements based on technical indicators, price levels, or other analytical data.
