Cryptocurrency Network Basics: How Nodes and Masternodes Work
Discover the hidden power behind cryptocurrency nodes and masternodes, the unsung heroes fueling the decentralized magic.
In this guide, we'll demystify a key component of the crypto universe by answering the question: What exactly is a crypto node?
The allure of cryptocurrency is not just in its potential profits, but also in the unique and captivating technology that underpins it. Although you can certainly ride the wave of bitcoin's rising value without delving into the intricacies of blockchain, arming yourself with fundamental knowledge of the concepts at play can prove invaluable.
So, buckle up and prepare to embark on an intriguing journey, as we delve into the cryptocurrency network basics and unveil the magic of nodes and masternodes.
What Are Cryptocurrency Nodes
A single computer that participates in and communicates with a blockchain network is known as a crypto node.
👉 At its core, a node is simply a device running the software of a specific blockchain. From routers and modems to switches, hubs, and servers, any device with an IP address can potentially serve as a node.
Blockchains are governed by a collective of users who operate nodes within the network. Each node is an individual computer containing the complete information of the blockchain, enabling it to authenticate and log new transactions in real-time before broadcasting them to the broader network.
In the absence of a centralized authority, this network of crypto nodes shoulders the responsibility of recording fresh transactions and maintaining the updated shared ledger. Nodes also help filter out transactions that may be attempting to deceive the system or violate established rules.
The presence of a larger number of crypto nodes makes it increasingly challenging to manipulate the entire system, as an attacker would need to compromise every single node to succeed — a feat that is virtually impossible.
The variety of node types hinge on the architecture and design requirements of a particular blockchain protocol. Each type contributes its own distinct function in sustaining the blockchain ecosystem's smooth operation.
👉 Connecting to a network is akin to surfing the internet. Nodes act much like a browser, as they are familiar with the specific network protocol and can interact with other nodes in the system.
Participation in a protocol is also voluntary – with nothing on the line, nodes have the freedom to leave the network whenever they choose.
Types of Nodes in Cryptocurrency
In general, nodes can be categorized as full nodes or lightweight nodes.
- Full nodes serve to fortify the network by downloading the entire blockchain history, enabling them to enforce rules and monitor activity.
- Lightweight nodes, conversely, shoulder a lighter workload and rely on full nodes to function properly. Given their essential role in a blockchain's operation, numerous volunteers run full nodes to bolster the ecosystem. However, it's worth noting two additional sub-types of nodes: listening nodes (also known as supernodes) and miner nodes.
- Listening nodes are public full nodes that volunteers operate to support the Bitcoin and crypto ecosystem. These nodes communicate with any other node that connects to them, verifying transactions and bolstering blockchain security.
- Since miners are part of the larger blockchain system, they also function as nodes. Miner nodes can be solo nodes, with the miner running the node on their device, or they can participate in mining pools where multiple people pool their computing power to mine bitcoin and verify transactions.
👉 If in proof-of-work (PoW), miners function as nodes, in proof-of-stake (PoS), staking wallets take on the role of nodes.
Bear in mind that each blockchain network may exhibit minor or significant structural differences, leading to variations in the roles and responsibilities of the general node types described here.
However, it's essential to highlight the one common thread uniting all nodes: they all execute the software, often referred to as the protocol, which defines a specific blockchain's rules, features, and functionality.
How Do Crypto Nodes Work?
Crypto nodes are essential components of blockchain networks that perform various functions to maintain the system's integrity, security, and functionality. Here's how crypto nodes work:
- Maintenance: Nodes act as guardians of a blockchain, synchronizing all ledger copies, storing encrypted data from past transactions, and accommodating new blocks for scalable growth.
- Validation: Peer nodes verify transaction signatures, prevent double-spending, and confirm that new blocks are mined according to the network's protocol.
- Consensus: Nodes are designed to process transactions based on majority consensus. They act as impartial judges, working together to establish a fair and accurate state of the blockchain. By adhering to a set of rules, such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), nodes reach a majority agreement on the content of the blockchain.
- Propagation: Consensus mechanisms ensure that all nodes stay in sync. New blocks are processed live, and all ledger copies are updated instantaneously. United in harmony, nodes collectively represent the network's true state.
- Accessibility: Nodes serve as friendly tour guides, providing access to the blockchain and helping users interact with the network. They offer information on transaction history, account balances, and network status, always ready to lend a helping hand.
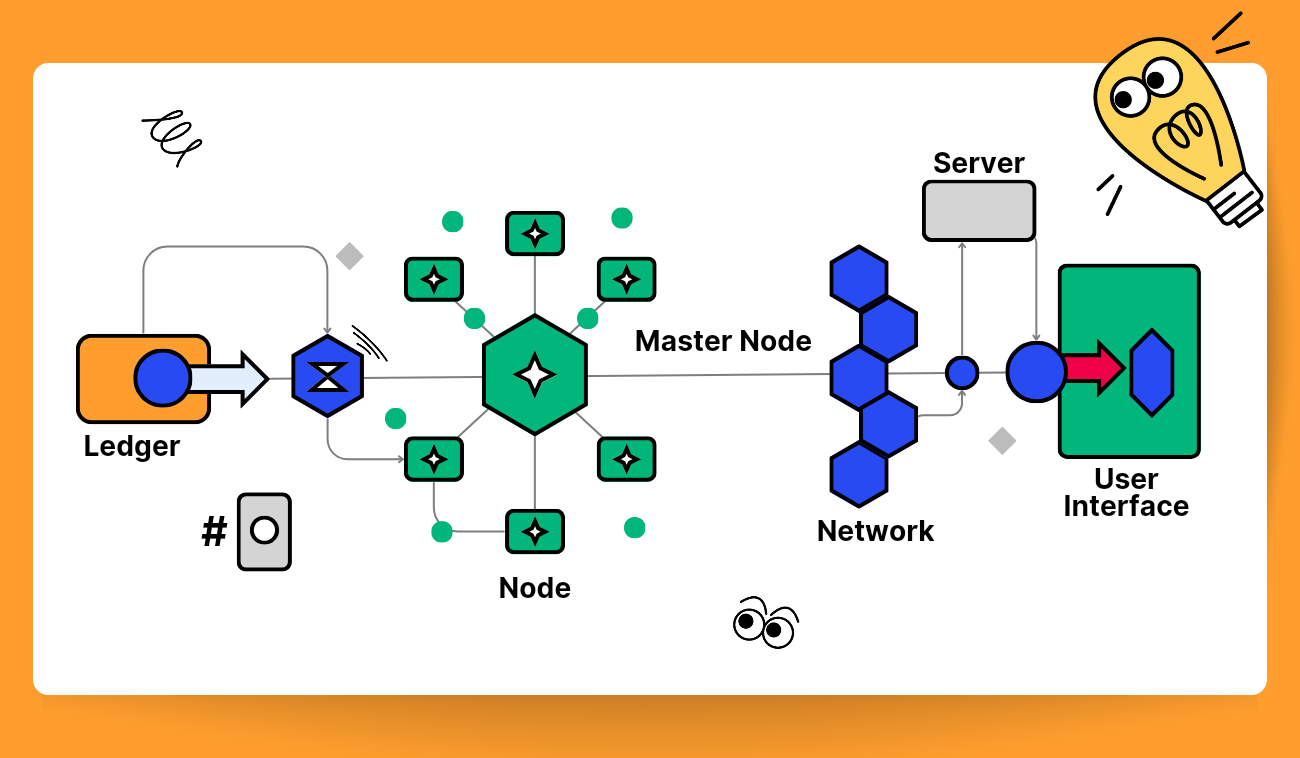
Node vs Masternode
Masternodes don't actually create new blocks but verify them instead. They also assume special management, governance, and regulatory roles based on the blockchain protocol they're part of. Masternodes first emerged in the Dash protocol in 2014 within a system called proof-of-service (PoSe). Although they're more commonly found in PoS ecosystems, they can also be used in PoW.
👉 Picture a crypto masternode as a server within the decentralized blockchain network it supports, holding a full copy of the blockchain ledger and taking on extra responsibilities. Depending on the blockchain in question, masternodes can oversee voting events and carry out protocol operations.
Crypto masternodes operate within a collateral-based system akin to a PoS protocol. Operators must possess a substantial amount of the native cryptocurrency to run a masternode. In exchange, they receive guaranteed annual coin earnings for their services. This approach ensures that the network's most crucial nodes are financially motivated, ultimately reinforcing network stability and loyalty. Consequently, masternodes are also referred to as bonded validator systems, echoing the logic behind staking in a PoS system.
How Does Crypto Masternode Work?
Running a masternode involves staking a set amount of coins as collateral, setting up a server, and being rewarded for providing services to the network. To understand how a masternode works, let's break down these key processes involved:
- Collateral is meant to increase the masternode operator's commitment to the network. So to join the masternode crew, you need to prove your loyalty by locking away some of your precious crypto coins. This guarantees that you will have a vested interest in the network's success and won’t engage in malicious activity.
- Masternodes run on dedicated servers, either physical or virtual, that need to stay online continuously. That implies your masternode must be either a shipshape physical or virtual private server (VPS) operating 24/7 to ensure smooth sailing.
- In return, masternode operators get periodic rewards in the form of coins from a portion of the mining rewards. That means you'll receive a share of the block rewards as a token of gratitude for your invaluable service. These rewards may vary across cryptocurrencies.
- Masternodes carry out critical functions like validating transactions, enabling instant transactions, increasing privacy through coin mixing, participating in governance votes, and more.
- To pick which masternode gets to perform tasks or collect rewards, there's a fair and square selection process. The crafty algorithm takes into account factors like the age of your collateral and a touch of randomness to level the playing field.
Examples of Nodes and Masternodes
Let’s chat about Bitcoin and Dash nodes as pertinent examples.
Bitcoin relies on a network of nodes that store the entire transaction history of the blockchain. However, it's the miners who verify transactions, create new blocks, and collect the fees associated with them. Operating a Bitcoin node by itself does not generate any income, unless you also engage in mining activities.
Dash, on the other hand, employs a two-tier network that includes both miners and masternodes. To run a Dash masternode, you must lock up 1,000 Dash coins as collateral. Masternodes play a crucial role in the network by storing the blockchain data, verifying transactions, and providing additional services like InstantSend and PrivateSend. Masternode operators receive rewards for their contribution to the network, which comes from a portion of the block rewards.
Masternodes Pros and Cons
Here’s a brief overview of the main benefits and drawbacks of setting up a masternode:
Advantages of masternodes:
- Earn cryptocurrency without investing in expensive mining equipment.
- Masternodes are more energy-efficient compared to mining, making them environmentally friendly.
- Hosting a masternode on a VPS is generally affordable.
- The learning curve for setting up and operating a masternode is manageable, and you don't need extensive specialized knowledge.
Disadvantages of masternodes:
- A substantial amount of cryptocurrency is required as collateral, which can be a significant upfront expense.
- Some masternode coins may struggle to maintain their value due to a continuous influx of easily obtainable coins, affecting the potential return on investment.
- If the network's difficulty increases or other factors impact the rewards, your profit potential may decrease over time.
How to Earn with Cryptocurrency Masternodes
You can earn cryptocurrency through masternodes by acquiring a specific number of coins as collateral and then hosting a masternode on a virtual private server (VPS). Since masternodes have relatively low system requirements, even a budget-friendly $5/month VPS plan can accommodate one, making it easier to achieve a profit.
Masternode coins often provide attractive returns, allowing you to generate extra income every month. You can find various websites that display the expected percentage returns for specific masternode coins, helping you calculate your potential profit margin.
Masternodes vs Staking
Masternodes and staking are two different ways to earn rewards in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. A masternode requires you to lock up a specific number of coins as collateral before you can start earning rewards. On the other hand, staking allows you to begin earning rewards with any number of coins, depending on the staking mechanism of the particular cryptocurrency.
Staking rewards are typically calculated based on factors such as your wallet balance (or weight), coin age, and network difficulty. These factors determine the amount and frequency of your rewards.
While setting up a masternode can be more expensive than staking, it can sometimes yield more consistent earnings. This is because not everyone can afford the required funds to establish a masternode, leading to less competition for rewards.
Masternodes vs Mining
Both mining and masternodes require upfront investments, with mining needing specialized hardware and masternodes requiring a certain amount of coins as collateral. Mining operations typically have higher ongoing costs due to energy consumption and hardware maintenance.
While mined coins often hold their value better, it's essential to monitor mining operations to ensure profitability. In contrast, masternodes are generally cheaper to run and easier to manage. However, the value of masternode coins can sometimes be unstable due to an influx of new coins entering the market, which may impact potential returns.
Wanna Trade Crypto?
On a somewhat tangential note — ever heard of Bitsgap?
Bitsgap is your one-stop shop for automated cryptocurrency trading that'll have you connected to the world's top exchanges faster than you can say "API."
With a smorgasbord of strategies, including GRID, DCA, BTD, and COMBO, plus smart trading extras like trailing and hedging, Bitsgap is your trusty sidekick in the digital currency arena.
Dip your toes in with a 7-day free trial and demo account, and trade confidently knowing that Bitsgap has your back. Embrace the future of investing and give it a whirl today!
FAQs
What Is Full Node?
A full node is a more dedicated participant in a cryptocurrency network and comes with certain privileges. When you run a full node, you have a sort of "voting right" in the event of a chain split, allowing you to decide which fork to follow based on your preference.
Full nodes also contribute to the security and integrity of the network. They reject invalid transactions and blocks, helping to maintain the robustness of your favorite cryptocurrency.
Running your own full node provides added privacy since it serves as a private connection point within the network. Some individuals operate a full node for enhanced security, even if they do not participate in mining.
To run a full node, you must meet the minimum system requirements, which include having the appropriate software and maintaining a constant internet connection.
What Is a Masternode?
A masternode is a type of node used in some proof-of-stake (PoS) cryptocurrency networks. Unlike regular nodes, masternodes often receive block rewards for their services. These nodes not only store and process blockchain information but also perform additional tasks such as verifying transactions, similar to miners in proof-of-work (PoW) cryptocurrencies.
Running a masternode is generally cheaper and easier to set up than a mining operation, making it an appealing option for individuals who wish to participate in a cryptocurrency network without extensive technical knowledge.
