
Understanding Market Order in Crypto Trading
Like a raging bull let loose in a china shop, market orders can help you swiftly seize the crypto coins you covet. Harness their speed to outpace the herd by learning how market orders work and expert strategies for deploying them in your crypto trading.
For crypto cowboys chasing fast gains, market orders are your rocket ships to instantly lasso coveted coins before the herd snatches them up. But dashing into trades without a strategy can lead to getting trampled, so study up to become a top crypto trader.
Cryptocurrency trading involves placing orders, which are directives you provide to exchanges for purchasing or selling digital assets. These orders can range from immediate trades to those contingent upon certain conditions being fulfilled. In this article, we’ll deal with the former — a market order — the simplest type of order to buy or sell immediately at an asset’s current price.
Read on to learn more about market orders, when to employ them, and how they differ from other order types in the dynamic world of crypto.
What Is Market Order in Crypto Trading?
A market order represents a directive to promptly purchase or sell at the best available price.
👉 For instance, imagine that the price of BTC is surging swiftly, and you desire to acquire it without delay. You are content with the market's price, provided you can obtain your coveted asset immediately. Under such circumstances, you would initiate a market order on your preferred exchange.
Its execution relies on liquidity, as it is fulfilled according to the limit orders already present in the order book.
But in contrast to limit orders, where a cryptocurrency is traded only at a predetermined price, market orders are executed instantly at the most favorable current price. Traders who agree to a market order commit to selling at the bid price or buying at the ask price. This differs significantly from limit orders, which are used by traders to purchase crypto assets when a specific price is reached — a useful strategy when anticipating price drops.
If your goal is to buy or sell instantly at the prevailing market rate, a market order serves as an optimal choice.
However, a potential drawback of market orders is their possible negative impact on price-sensitive traders, who might agree to a higher price only to see the market order filled as the exchange seeks the most advantageous price.
How Does a Market Order Work?
Unlike the patient approach of limit orders, which await their turn on the order book, market orders leap into action, instantly seizing the current market price.
In every trade, there are two parties: the maker and the taker. By placing a market order, you accept the price established by another party. For example, an exchange will expertly pair a buy market order with the lowest ask price on the order book's floor, while a sell market order will find its perfect partner in the highest bid price.
As we've mentioned earlier, market orders depend on the pulsating energy of liquidity surging through the exchange's order book, meeting the demands of the moment. Since market orders remove liquidity from the exchange, you will incur higher fees as a market taker when executing one.
Market Order Example
Our buddy Jimmy was riding the crypto rollercoaster all day, watching his holdings go up and down like a yo-yo. He's managed to pocket a tidy sum, but suddenly, the alarm bells start ringing. His trusty technical analysis whispers a dire warning: "sell, sell, sell!"
Now Jimmy didn't want to lose his hard-earned gains, so he slammed that market sell button to cash out pronto. The price kept dropping, but he managed to escape with just a 10% haircut on his holdings.
If he had tried to set a limit order instead, he might've gotten crushed by 30% or more. Good thing Jimmy used that market-order lifeboat when he did!
Market Order vs Limit Order
As mentioned, limit orders are directives to buy or sell a specific amount of a financial asset at a predetermined price or better. You can decide whether the exchange can partially fulfill your limit order or if it must be filled entirely. If the latter, and the exchange cannot fully fill your order, it won't be executed at all.
Market orders can only be completed with existing limit orders. For those who prefer not to accept the current market price when trading or investing, limit orders serve as a practical alternative. Limit orders allow you to plan your trades in advance without the need to actively monitor them.
Beyond these fundamental differences, market orders and limit orders cater to distinct trading activities and objectives. Limit orders are typically more suitable in volatile markets, for assets with low liquidity, and if your strategy involves scenarios when you’re not actively trading.
Market Order vs Stop Loss
A stop-loss order helps you minimize potential losses on an investment by automatically triggering a market order once the asset's price reaches a predetermined stop point. If the asset's price decides to tumble past that point, your stop-loss order morphs into a market order.
The exchange will then attempt to liquidate your holdings at the best available price to protect your capital. While a market order can also be used to sell your holdings, it requires manual execution and is more suitable for immediate transactions, unlike a stop-loss order, which is set in advance and activated only when the stop price is reached.
When to Use Market Orders: Market Order Use Cases in Crypto Trading
Market orders swoop in to save the day when filling an order takes precedence over securing a specific price. That means you should only unleash market orders if you're ready to embrace the potential higher costs due to slippage. In a nutshell, market orders are your go-to option when you're racing against the clock. Picture this: you had a stop-limit order that was passed over, and now you need to buy or sell ASAP. That's when market orders ride in to help you hop into a trade right away.
When trading highly liquid assets with a slim bid-ask spread, a market order can fetch you a price that's close to, or even right on, the anticipated spot price. However, assets with a wider spread are more likely to cause slippage, so proceed with caution.
👉 Pro tip: Finally, if you’re looking to buy bitcoin with altcoins, stick to limit orders, as market orders could leave you paying more than necessary.
How to Place a Market Order
Placing a market order is a piece of cake. Instead of specifying a particular price, you simply choose the market order option. Enter the quantity of coins or tokens you wish to acquire, and the exchange will handle the rest for you.
👉 However, be cautious, as the market's liquidity can impact the final price. You might end up paying more than you initially planned. To avoid any surprises, review the order book to estimate your potential costs before submitting your order.
Let’s see how you can place a market order on Bitsgap.
Start by navigating to the [Trading] tab on the platform, and then click [Market] located on the right side of your screen. You can either enter an amount manually or opt for a percentage of your portfolio (Pic. 1). Additionally, you can elevate your market order to a smart order by activating trailing and hedging features like "Take Profit," "Trailing Take Profit," and "Stop Loss."
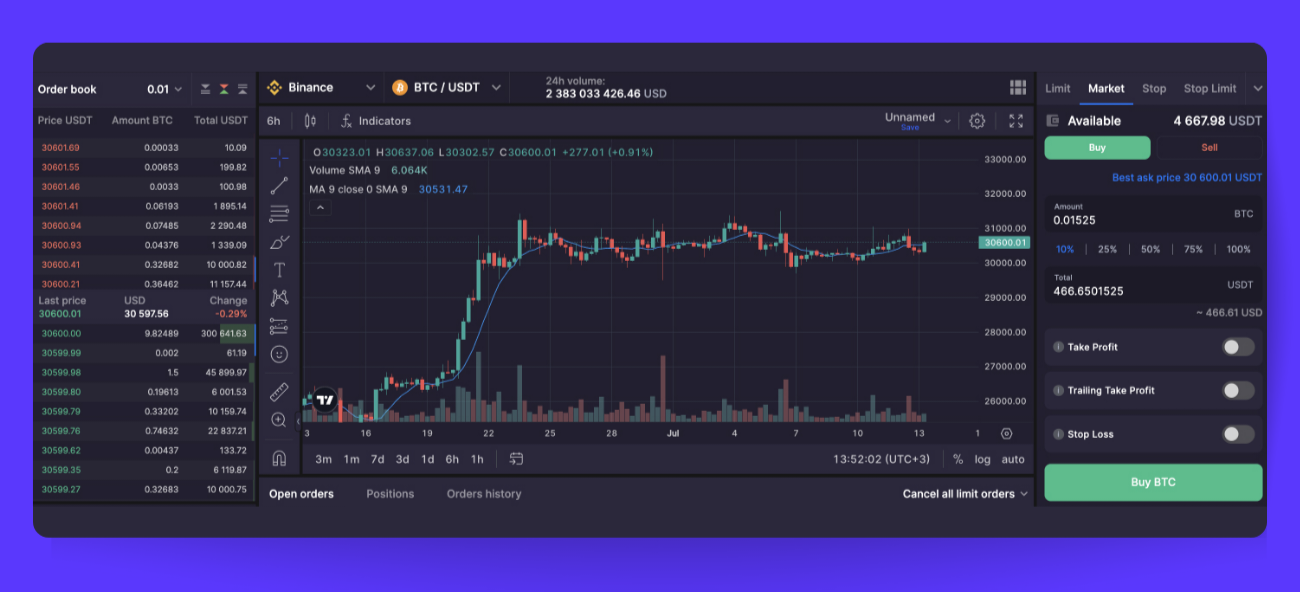
Interested in learning more about Trailing? Peruse this piece on the Help Center at your leisure.
See, Bitsgap isn't just another run-of-the-mill exchange. No, it's so much more. It's a renowned crypto aggregator that brings together over 15 exchanges, all under one accessible and streamlined platform. And it's not just us saying it — 500,000 traders can vouch for their satisfaction with our service.
But that's not all. Beyond manual trading, Bitsgap equips you with an impressive range of top-notch trading bots. From GRID to DCA, these bots are ready to help you navigate any market scenario. They're designed to help you maximize your profits and minimize losses. So, why wait? Step into the world of Bitsgap and let's start making your crypto trading journey a success!
Can Crypto Market Orders Be Canceled?
In most instances, market orders are filled almost instantaneously, making it extremely difficult to cancel them once they're in progress. If you attempt to sell or buy back coins and tokens using this method, you may face challenges, as you could be forced to either accept a loss or pay a premium in many cases.
However, if you're using market orders as a means of capital preservation, you might find opportunities to repurchase the assets at a lower price after a market drop.
Why Market Order May Not Be Filled?
In certain situations, an exchange may apply a "collar" to your market order. This is essentially a market order with a 5% price buffer, which means that if the price of the asset moves beyond 5% of the price at which you submitted your market order, it may not be executed.
While this is intended to safeguard investors, it may cause inconvenience if you are unaware of how your chosen exchange operates.
Market Order Risks and Benefits
Crypto market orders make a great choice for traders who don't want to wait around for a target price. Unlike other orders that hinge on the hope that the price will reach a specific target, market orders come with the assurance of being filled.
However, slippage poses a major challenge for market orders. Slippage occurs when a large market order is filled at multiple prices in the order book, resulting in an execution price that is worse than expected. This happens because there is not enough liquidity to fully fill the order at the desired price level. For small orders, slippage may be negligible, but for large orders, it can significantly impact results.
Liquidity and accurate trading volumes remain ongoing concerns in cryptocurrency markets. Some experts believe that reported volumes may be inflated or falsified.
In general, traders looking for greater control over their trading strategies might opt for limit orders.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, market orders offer a straightforward and efficient way to buy and sell financial assets, making them ideal for instant market entry or exit. However, this convenience comes at the expense of the precise control offered by other order types. To make the most of your trading experience, carefully evaluate your unique circumstances and determine when a market order is the right choice or when an alternative approach may better suit your needs.
FAQs
How to Use Market Orders in Crypto?
Using market orders in crypto trading is a straightforward process that enables quick buying or selling of assets. For example, on Bitsgap, you’ll navigate to the [Trading] tab, select your preferred exchange and trading pair, choose the [Market] order option amongst the available order types to the right, specify the amount, and toggle any other fancy features that’d make your market order a smart one. Most market orders are filled almost instantly. You can check the status of your order in the platform’s [Orders history] tab.
What Are Some Market Order Strategies?
A few good market order strategies include:
- Flash entry or exit: When every second counts and you're itching to jump in or out of a position, market orders swoop in as your trusty sidekick. Especially handy for trading liquid assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum, market orders allow for swift and seamless execution.
- Stop loss: This market order strategy is designed to shield you from excessive losses if the market rebels against your position. When your asset hits a specific price, the market order pounces into action, closing your position automatically. Be sure to set your stop loss strategically to avoid being booted out prematurely.
- Trailing stop: This market order strategy helps you lock in profits while keeping losses at bay. Set your stop loss at a specific percentage or dollar amount beneath the current market price, and watch it climb as the asset's price soars. If the market takes a turn for the worse, your stop loss will kick in at a higher price, capturing more profits.
- Market making: This strategy is all about placing buy and sell orders on both sides of the order book, conjuring liquidity and profiting from the bid-ask spread. Market makers often rely on market orders to swiftly enter or exit positions as needed.
